Starwhale Dataset User Guide
Design Overview
Starwhale Dataset Positioning
The Starwhale Dataset contains three core stages: data construction, data loading, and data visualization. It is a data management tool for the ML/DL field. Starwhale Dataset can directly use the environment built by Starwhale Runtime, and can be seamlessly integrated with Starwhale Model and Starwhale Evaluation. It is an important part of the Starwhale MLOps toolchain.
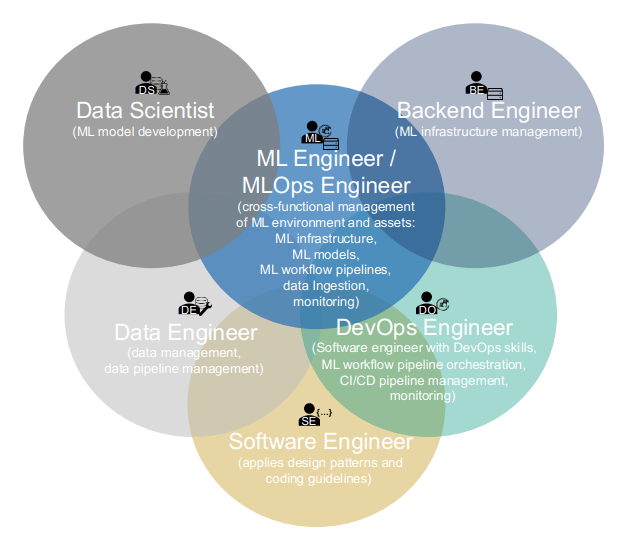
According to the classification of MLOps Roles in Machine Learning Operations (MLOps): Overview, Definition, and Architecture, the three stages of Starwhale Dataset target the following user groups:
- Data construction: Data Engineer, Data Scientist
- Data loading: Data Scientist, ML Developer
- Data visualization: Data Engineer, Data Scientist, ML Developer
Core Functions
- Efficient loading: The original dataset files are stored in external storage such as OSS or NAS, and are loaded on demand without having to save to disk.
- Simple construction: Supports one-click dataset construction from Image/Video/Audio directories, json files and Huggingface datasets, and also supports writing Python code to build completely custom datasets.
- Versioning: Can perform version tracking, data append and other operations, and avoid duplicate data storage through the internally abstracted ObjectStore.
- Sharing: Implement bidirectional dataset sharing between Standalone instances and Cloud/Server instances through the
swcli dataset copycommand. - Visualization: The web interface of Cloud/Server instances can present multi-dimensional, multi-type data visualization of datasets.
- Artifact storage: The Standalone instance can store locally built or distributed swds series files, while the Cloud/Server instance uses object storage to provide centralized swds artifact storage.
- Seamless Starwhale integration:
Starwhale Datasetcan use the runtime environment built byStarwhale Runtimeto build datasets.Starwhale EvaluationandStarwhale Modelcan directly specify the dataset through the--datasetparameter to complete automatic data loading, which facilitates inference, model evaluation and other environments.
Key Elements
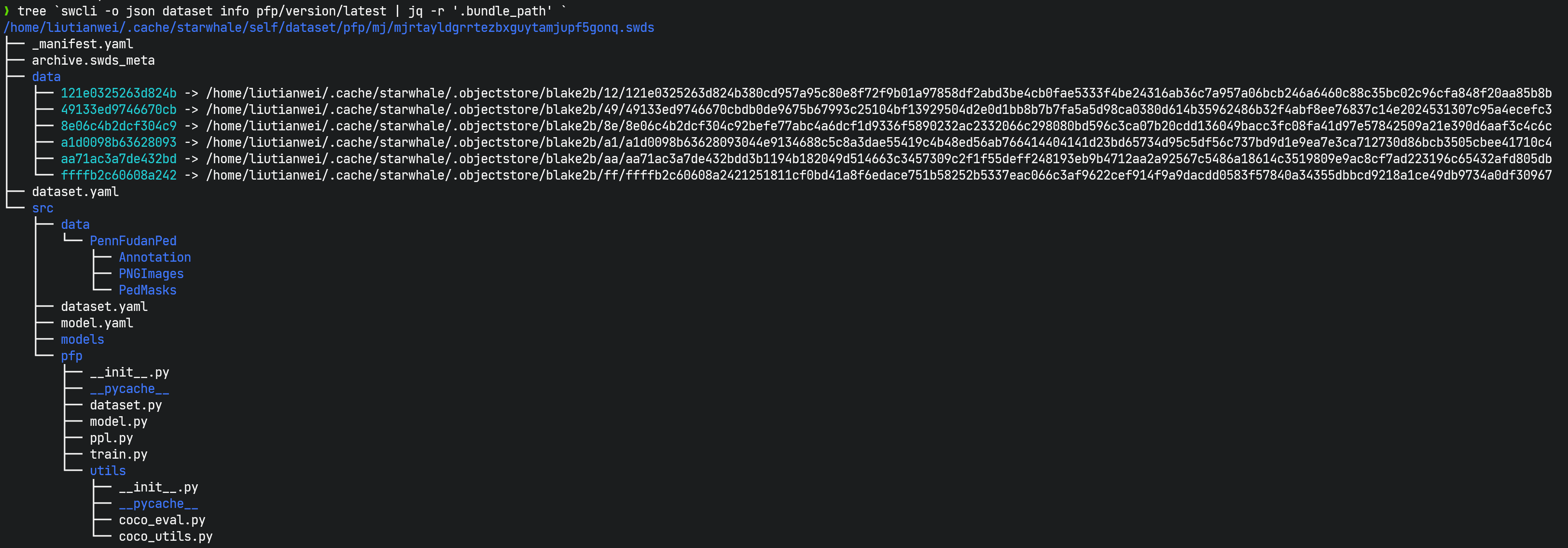
swdsvirtual package file:swdsis different fromswmpandswrt. It is not a single packaged file, but a virtual concept that specifically refers to a directory that contains dataset-related files for a version of the Starwhale dataset, including_manifest.yaml,dataset.yaml, dataset build Python scripts, and data file links, etc. You can use theswcli dataset infocommand to view where the swds is located. swds is the abbreviation of Starwhale Dataset.
swcli datasetcommand line: A set of dataset-related commands, including construction, distribution and management functions. See CLI Reference for details.dataset.yamlconfiguration file: Describes the dataset construction process. It can be completely omitted and specified throughswcli dataset buildparameters.dataset.yamlcan be considered as a configuration file representation of theswcli dataset buildcommand line parameters.swcli dataset buildparameters take precedence overdataset.yaml.- Dataset Python SDK: Includes data construction, data loading, and several predefined data types. See Python SDK for details.
- Python scripts for dataset construction: A series of scripts written using the Starwhale Python SDK to build datasets.
Best Practices
The construction of Starwhale Dataset is performed independently. If third-party libraries need to be introduced when writing construction scripts, using Starwhale Runtime can simplify Python dependency management and ensure reproducible dataset construction. The Starwhale platform will build in as many open source datasets as possible for users to copy datasets for immediate use.
Command Line Grouping
The Starwhale Dataset command line can be divided into the following stages from the perspective of usage phases:
- Construction phase
swcli dataset build
- Visualization phase
swcli dataset diffswcli dataset head
- Distribution phase
swcli dataset copy
- Basic management
swcli dataset tagswcli dataset infoswcli dataset historyswcli dataset listswcli dataset summaryswcli dataset removeswcli dataset recover
Starwhale Dataset Viewer
Currently, the Web UI in the Cloud/Server instance can visually display the dataset. Currently, only DataTypes using the Python SDK can be correctly interpreted by the frontend, with mappings as follows:
- Image: Display thumbnails, enlarged images, MASK type images, support
image/png,image/jpeg,image/webp,image/svg+xml,image/gif,image/apng,image/avifformats. - Audio: Displayed as an audio wave graph, playable, supports
audio/mp3andaudio/wavformats. - Video: Displayed as a video, playable, supports
video/mp4,video/aviandvideo/webmformats. - GrayscaleImage: Display grayscale images, support
x/grayscaleformat. - Text: Display text, support
text/plainformat, set encoding format, default is utf-8. - Binary and Bytes: Not supported for display currently.
- Link: The above multimedia types all support specifying links as storage paths.
Starwhale Dataset Data Format
The dataset consists of multiple rows, each row being a sample, each sample containing several features. The features have a dict-like structure with some simple restrictions [L]:
- The dict keys must be str type.
- The dict values must be Python basic types like int/float/bool/str/bytes/dict/list/tuple, or Starwhale built-in data types.
- For the same key across different samples, the value types do not need to stay the same.
- If the value is a list or tuple, the element data types must be consistent.
- For dict values, the restrictions are the same as [L].
Example:
{
"img": GrayscaleImage(
link=Link(
"123",
offset=32,
size=784,
_swds_bin_offset=0,
_swds_bin_size=8160,
)
),
"label": 0,
}
File Data Handling
Starwhale Dataset handles file type data in a special way. You can ignore this section if you don't care about Starwhale's implementation.
According to actual usage scenarios, Starwhale Dataset has two ways of handling file class data that is based on the base class starwhale.BaseArtifact:
- swds-bin: Starwhale merges the data into several large files in its own binary format (swds-bin), which can efficiently perform indexing, slicing and loading.
- remote-link: If the user's original data is stored in some external storage such as OSS or NAS, with a lot of original data that is inconvenient to move or has already been encapsulated by some internal dataset implementation, then you only need to use links in the data to establish indexes.
In the same Starwhale dataset, two types of data can be included simultaneously.